Unreal Engine has a useful feature called AsyncTask that allows you to execute code asynchronously via Task Graph system. It functions by running specific code on a specified thread and is primarily used when the task is too heavy to be executed instantly without blocking the game thread.
AsyncTask(ENamedThreads::AnyThread, []()
{
// This code will run asynchronously, without freezing the game thread
});
You can also create nested calls to asynchronous tasks, for example:
AsyncTask(ENamedThreads::AnyThread, []()
{
// This code will run asynchronously, without freezing the game thread
AsyncTask(ENamedThreads::GameThread, []()
{
// This code will be executed on the game thread
});
});
You can also combine this with delegates and execute your code asynchronously with Blueprints
#include "Async/Async.h"
DECLARE_DYNAMIC_DELEGATE_OneParam(FAsyncDelegateExample, const TArray<float>&, OutData);
// Class, meta, etc
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable)
static void AddNumbersAsync(TArray<float> InData, const FAsyncDelegateExample& Result)
{
AsyncTask(ENamedThreads::AnyThread, [InData = MoveTemp(InData), Result]() mutable
{
// Just for example
for (float& InDataElement : InData)
{
InDataElement += 10;
}
AsyncTask(ENamedThreads::GameThread, [OutData = MoveTemp(InData), Result]() mutable
{
Result.ExecuteIfBound(OutData);
});
});
}
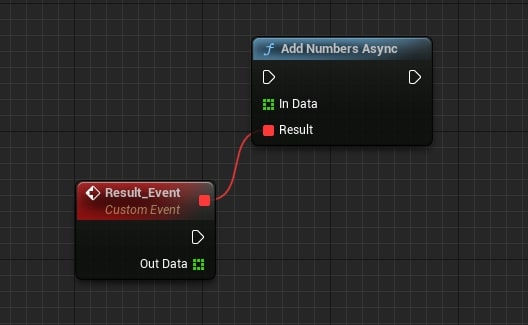
Useful notes:
GameThreadhas a dedicated thread, whereasAnyThread,AnyHiPriThread, etc., use available threads from the pool.- There’s
Asynctemplate function that is more flexible in some cases compared toAsyncTask(e.g., you can choose to execute the task in the thread pool, or to execute a callback when the task is done by the returnedTFutureobject), but is more limited to choosing the thread for the Task Graph system. Asyncprovides more flexibility compared toAsyncTask, especially with thread selection and callback handling.- Starting from UE 5.0, consider using the new Task Graph system for improved performance and flow in gameplay tasks: Tasks System docs .